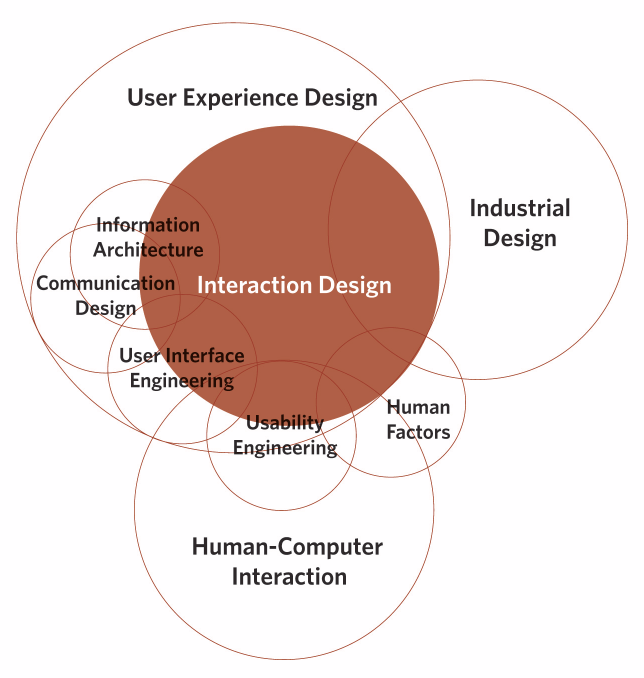
The process of interaction design involves studying the behavior and structure of interactive systems and implementing them for developing useful digital products. In other words, interaction design is the relationship between user and product and the services they use.
The purpose of interaction design is to create a great user experience. That’s why most of the UI disciplines require understanding and hands-on experience of interaction design principles. After all, it’s about designing for the entire interconnected system: the device, interface, context, environment, and people. Interaction designers strive to create meaningful relationships between people and the products and services they use. It may include computers, mobile devices, gadgets, appliances, and more.
It is important to understand ux design best practices while developing complex web and mobile applications. These are the key elements that product designers should not neglect while creating an interface for the user.
The 10 most important interaction design principles are-
- UX: Match user experience and expectations
- Consistent design: Maintain consistency throughout the application
- Functionality: Follow functional minimalism
- Cognition: Reduce cognitive loads/mental pressure to understand the application
- Engagement: Design interactively such that it keeps the user engaged.
- User control: Allow the user to control, trust, and explore
- Perceivability: Invite interactions through intuitions and interactive media
- Learnability: Make user interactions easy to learn and remember
- Error handling: Take care to prevent errors, if they occur make sure to detect and recover them.
- Affordability: Simulate actions by taking inspiration from usual and physical world interactions.
10 Important Interaction Design Principles
#1 Match user experience and expectations
By matching the sequence of steps, layout of information, and terminology used with the expectation and prior experiences of the users, designers can reduce the friction and discomfort of learning a new system.
You can match your audience’s prior experiences and expectations by using common conventions or UI patterns, for example, Hitee Chatbot.
#2 Consistency
Along with matching people’s expectations through terminology, layout, and interactions, the design should be consistent throughout the process and between related applications.
By maintaining consistency, you are helping users learn more quickly. You can re-apply their prior experiences from one part of an application to another to maintain consistency throughout the design. Design consistency is also an aid to intuitive interfaces.
Bonus – you can use the inconsistencies to indicate to users where things might not work the way they expect. Breaking consistency is similar to knowing when to be unconventional.
#3 Functional minimalism
“Everything should be made as simple as possible, but no simpler.”
Albert Einstein
The range of possible actions should be no more than is absolutely necessary. Providing too many options will detract the primary function and reduce usability by overwhelming the user with choices. To achieve the Zen of functional minimalism, you should-
- Avoid unnecessary features and functions
- Break complex tasks into manageable sub-tasks
- Limit functions rather than the user experience.
#4 Cognitive loads
Cognition refers to the “process of thoughts.” A good user interactive design minimizes the user’s “effort to think” to complete a task. Another way to put this is that a good assistant uses his skills to help the master focus on his skills.
For instance, while designing an interactive interface, we need to understand how much concentration a task requires to complete it. Accordingly, you can design the UI that reduces the cognitive load as much as possible.
Here’s a technique to reduce users’ “thinking work.” Focus on what the computer is good at and build a system that utilizes its abilities to the fullest. Remember, computers are good at-
- Maths
- Remembering things
- Keeping track of things
- Comparing things
- Spell Checking and spotting/correcting errors
The point is – by knowing the attributes of users and products, one can create a design for a better user experience.
#5 Engagement
In terms of user experience, engagement is the measure of the extent to which the user has a positive experience with your product. An engaging experience is not only enjoyable but also easier and productive. Engagement is subjective to the system. I.e. your design must engage with the desired audience. For instance, what appeals to teenagers might be irrelevant to their grandparents. Apart from aligning your design for the appropriate audience, achieving and creating control is the key.
The interaction design principles state that users should always feel like they’re in control of the experience. They must constantly experience a sense of achievement through positive feedback/results or feel like they’ve created something.
In his book “Flow,” Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi describes a state of optimal experience where people are so engaged in the activity that the rest of the world falls away. Flow is what we’re looking to achieve through engaging interactions. We should allow users to concentrate on their work and not on the user interface. In short, stay out of the way!
#6 Control, trust, and explorability
Good interaction design should incorporate control, trust, and explorability to any system. If users feel in control of the process, they’ll be more comfortable using the system. If the user is comfortable and in control, they’ll trust the system and believe that the application will prevent them from making an unrecoverable error or from feeling stupid. Trust inspires confidence and with confidence, the user is free to explore further. Intuitive interfaces are extremely good at stimulating users to navigate and explore the app.
#7 Perceivability
People are aware of the opportunity to interact with interactive media. As interface designers, we must avoid developing hidden interactions, which decrease the usability, efficiency, and user experiences. In other words, people should not have to guess or look for opportunities to interact.
When developing interactive media, users should have the ability to review an interface and identify where they can interact. We must remember that not everyone experiences and interacts with interface in the same way others do. In the process of interaction design, make it a habit to provide hints and indicators like buttons, icons, textures, textiles, etc. Let the user see that these visual cues can be clicked or tapped with their fingers. Always consider the usability and accessibility of the interactive media and how the user sees and perceives the objects in the interface.
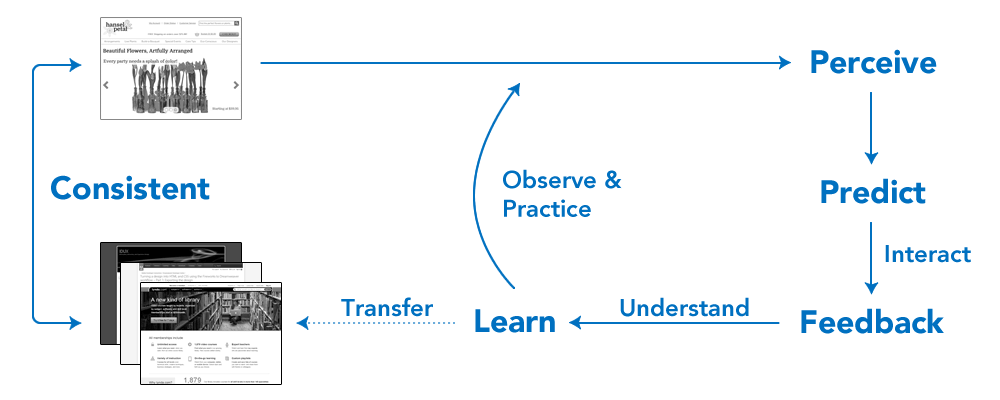
#8 Learnability
Another important interaction design principle is inducing the ability to learn to use the interface easily. In other words, users should be able to learn to use the interface in the first attempt and should not face issues using it again. Please note that engaging interfaces allow users to easily learn and remember the interactions.
Even though simple interfaces may require a certain amount of experience to learn, learnability makes interaction intuitive. People tend to interact with an interface similar to other interfaces. This is the reason why we must understand the process of interaction design thoroughly and the importance of design patterns and consistency.
Intuitive interface design allows users to learn to use the interface without much effort and gives them a sense of achievement. They feel smart and capable of grasping and utilizing newer interfaces. In a nutshell, product designers should let the user feel confident while navigating through the interface.
#9 Error prevention, detection, and recovery
The best way to reduce the number of errors a user makes is to anticipate possible mistakes and prevent them from happening in the first place. If the errors are unavoidable, we need to make them easy to spot and help the user to recover from them quickly and without unnecessary friction.
Error prevention techniques-
- Disabling functions that aren’t relevant to the user
- Using appropriate controls to constrain inputs (e.g. radio buttons, dropdowns, etc.)
- Providing clear instructions and preemptive help
- As a last resort, provide clear warning messages.
How to handle application errors through design?
Anticipate possible errors and provide feedback that helps users verify that-
- They’ve done what they intended to do.
- What they intended to do was correct.
Please note that providing feedback by changing the visuals of the object is more noticeable than a written message.
Error recovery techniques –
If the error is unavoidable, provide direction to the user to recover from it. For example, you can provide “back,” “undo,” or “cancel” buttons.
If a specific action is irreversible, you should flag it “critical” and make the user confirm first to prevent slip-ups. Alternatively, you can create a system that naturally defaults to a less harmful state. For example, closing a document without saving it should be intelligent enough to know the unlikely behavior of the user. It can either auto-save or display a warning.
#10 Affordance
Affordance is the quality of an object that allows an individual to perform an action. For example, a standard household light switch appears innately clickable.
The point is – users should get a clue about how to use an abject through its physical appearance. While designing user interfaces, you can achieve affordance either by simulating ‘physical world’ affordances (e.g. buttons or switches) or keeping consistency with web standards and interface design elements (e.g. underlined links or default button styles). The thing is, in an intuitive interface, users are able to navigate and use the functionalities of the application without any formal training.
Interaction design is not always about creating a better interface for the users; it is also about using technology in the way people want. It is necessary to know the target users to design a desirable product for them. Interactive design is the basis for the success of any product. These 10 interaction design principles are based on the study and experiences of our team in designing mobile and web apps for a broad product portfolio and on multiple mobile and web platforms.
Drop us a word at hello@mantralabsglobal.com to learn more about our interaction design projects and services.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox





