One of Japan’s leading insurance firms — Fukoku Mutual Life Insurance claims to have replaced 34 human tasks with IBM Watson (AI technology).
Cognitive automation is a subset of artificial intelligence that uses advanced technologies like natural language processing, emotion recognition, data mining, and cognitive reasoning to emulate human intelligence. In simple words, cognitive automation uses technology to solve problems with human intelligence.
The main pillars of cognitive automation
Consider an automated home security system programmed to function based on millions of decisions. It may still encounter situations when it does not know what to do. Machines can make logical decisions in many unforeseen situations using cognitive neuroscience.
The technologies to make cognition-based decisions possible include natural language processing, text analytics, data mining, machine learning, semantic analytics, and more. The following table gives an overview of the technologies used in cognitive automation.
| TECHNOLOGY | DESCRIPTION |
| Machine Learning | It involves improving a system’s performance by learning through real-time interactions and without the need for explicitly programmed instructions. |
| Data Mining | It is the process of finding meaningful correlations, patterns, and trends from data warehouses/repositories using statistical and mathematical techniques. |
| Natural Language Processing | NLP is a computer’s ability to communicate with humans in native languages. |
| Cognitive Reasoning | It is the process of imitating human reasoning by engaging in complex content and natural dialogues with people. |
| Voice Recognition | It is transcribing human voice and speech and translating it into text or commands. |
| Optical Character Recognition | It uses pattern matching to convert scanned documents into corresponding computer text in real-time. |
| Emotion Recognition | It is the understanding of a person’s emotional state during voice and text-based interactions. |
| Recommendation Engine | It is a framework for providing insights/recommendations based on different data components and analytics. For instance, Amazon was one of the first sites to use recommendation engines to make suggestions based on past browsing history and purchases. |
Why is cognitive process automation important for enterprises?
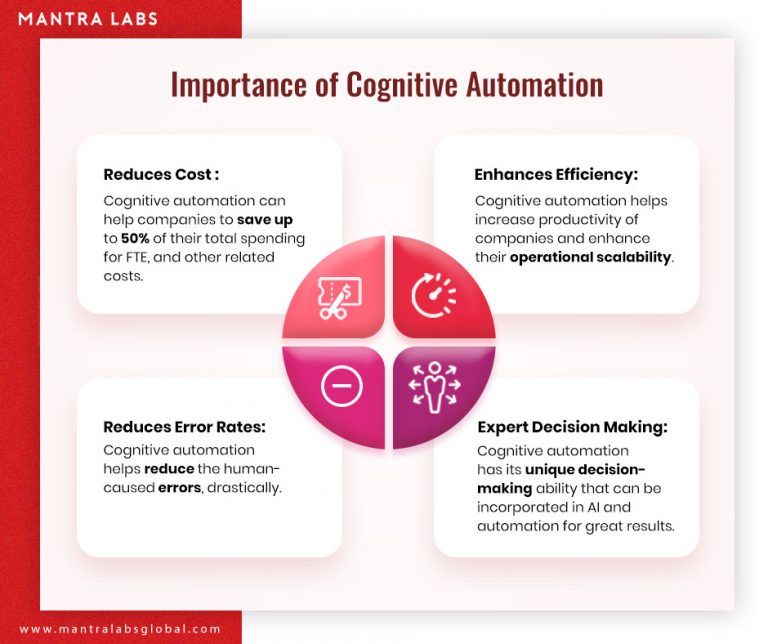
Cognitive automation improves the efficiency and quality of computer-generated responses. In fact, cognitive processes are overtaking nearly 20% of service desk interactions. The following factors make cognitive automation next big enhancement for enterprise-level operations –
- Cost-effective: Cognitive automation can help companies to save up to 50% of their total spending for FTE, and other related costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation can enhance employee productivity, leading to better operational efficiency.
- Increased accuracy: Such systems are able to derive meaningful predictions from a vast repository of structured and unstructured data with impeccable accuracy.
- Facts-based decision making: Strategic business decisions drill down to facts and experiences. Combining both, cognitive systems offer next level competencies for strategic decision making.
Also read – Cognitive approach vs digital approach in Insurance
Applications of cognitive automation
End-to-end customer service
Enterprises can understand their customer journey and identify the interactions where automation can help. For example, Religare — a leading health insurance company incorporated NLP-powered chatbot into their operations and automated their customer-support and achieved almost 80% FTE savings. Processes like policy renewal, customer query ticket management, handling general customer queries at scale, etc. are possible for the company through chatbots.
Processing transactions
Reconciliation is a tedious yet crucial transaction process. Banking and financial institutions spend enormous time and resources on the process. Paper-based transactions, different time zones, etc. add to the complicacy of settling transactions. With human-like decision-making capabilities, cognitive automation holds a huge prospect of simplifying the transaction-related processes.
Claims processing
In insurance, claims settlement is a huge challenge as it involves reviewing policy documents, coverage, the validity of insured components, fraud analytics, and more. Cognitive systems allow making automated decisions in seconds by analyzing all the claims parameters in real-time.
Also read – How intelligent systems can settle claims in less than 5 minutes
Requirements
Deloitte’s report on how robotics and cognitive automation will transform the insurance industry states that soon, automation will replace 22.7 million jobs and create 13.6 million new jobs. However, not all operations can be automated. The following are the requirements for successfully automating processes.
- Input sources: The input sources should be machine-readable, or needs to be converted into one. Also, there’s a limitation to the number of sources that the system can process for decision making. For instance, in an email management process, you cannot automate the resolution of every individual email.
- Availability of the technology: Cognitive automation combines several technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, analytics, etc. Thus, all the technologies should be available to make automated processes functional.
- Data availability: For the cognitive system to make accurate decisions, there should be sufficient data for modeling purposes.
- Risk factor: Processes like underwriting and data reconciliation are good prospects of cognitive automation. However, based on the risk value and practical aspects, human intervention may be required to make the final decision.
- Transparency & control: Cognitive automation is still in a nascent stage and humans may overturn machine-made decisions. Therefore, the system design needs to adhere to transparency and control guidelines.
Wrapping up
Cognitive systems are great for deriving meaningful conclusions from unstructured data. Many back and front office operations can be automated for improving efficiency, especially in consumer-facing functions to understand requirements and feedback. For instance, cognitive automation comes with powerful emotion recognition capabilities. It can help with making sense of customer tweets, social updates, through face recognition and analyzing texts.
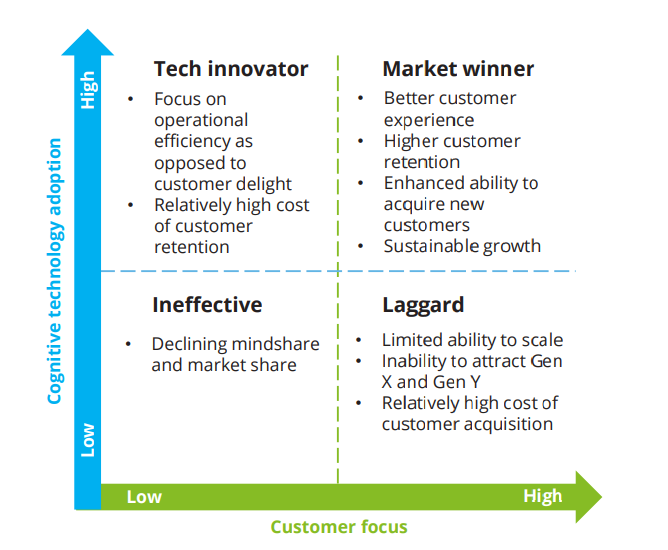
Since cognitive automation solutions help enterprises to adapt quickly and respond to new information and insights, it is becoming crucial for customer-centric businesses. The following graph shows how important cognitive technology adoption is for businesses that focus on consumer centricity.
Also read – 5 Front office operations you can improve with AI
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox





