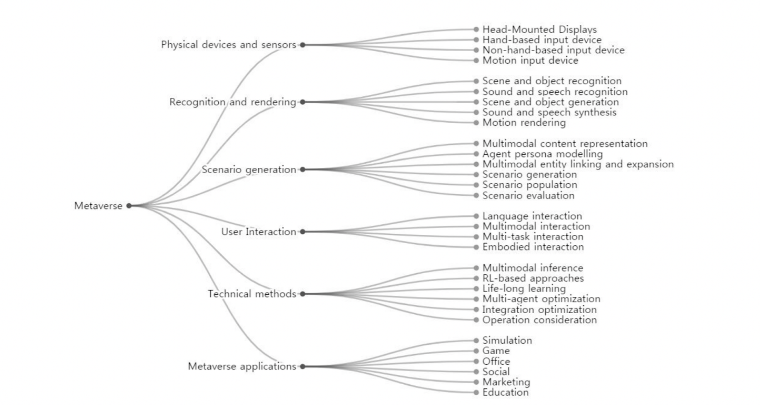
We’ve discussed blockchain, Metaverse, and Mixed Reality in our previous blogs showcasing perspectives from different industries on how this virtual world is helping businesses to boost customer experience.
But in order to give an exceptional user experience, it is imperative to know what its target audience wants in terms of design. What will be the role of design in web 3.0 and what will be the challenges in creating a good design for these users?
Since the 1990s the internet world has evolved three times: web 1.0 (1990-2004), web 2.0(2004-Current), & Web 3.0 ( New ).
Web 3.0 includes modern internet technologies such as blockchain, cryptocurrency, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), & Metaverse (AR, VR & Mixed Reality).
The newer target customers – millennials and Generation Z (also known as Internet Generation) are living in Web 3.0. Their life revolves around technology. What they want is a smarter and more intelligent experience. In the world of Web 3.0, customer experience (CX) is based on user recommendations, automatic chatbots, and advanced search results leveraging machine learning, improved connectivity etc.
Image Credit: Navdeep Yadav
Renowned companies like JPMorgan Chase, HSBC, Gucci, Coca Cola are dabbling in the Metaverse.
“According to citi report, the Metaverse could be an $8-13 trillion dollar market by 2030.”
Why should you care about ‘Web 3.0’ when designing?
Traction follows the money. That is why huge companies are interested in it. In order to give a web immersive experience to the current audience, we need to understand how designers can create web 3.0 experiences for the audience.
Design is at the forefront of global transition with a newer set of customer expectations driving the market. The challenges in designing for the metaverse (VR, AR & MR) are numerous, as there is no clearly defined solution. Here are a few points to keep in mind while designing for Web 3.0 users:
Design for Blockchain: For the design industry, there is no clarity about how designers can adapt to web3.0 trends for giving a better user experience. However, some industry leaders suggest that to develop a web 3.0 site, one must first understand blockchain technology from a design perspective, such as the challenges this technology can present. Because the audience is not aware of the blockchain’s advantages & limitations.
Designers can create web experiences by considering: visitors’ attention, simplifying complex elements, designing unique visual elements, maintaining a brand identity, and other things.
Design for VR: When a designer creates a VR experience for the users it is necessary to create a good immersive experience. Even though there is no final standard design guideline in the industry, what can be useful while designing is understanding people and the platform you design for, visualizing the interaction keeping user convenience at the center, considering head tracking, preventing motion sickness, and creating a guideline for the user.
Design for AR: While designing for AR, understanding the actual problem and ensuring that AR is the right channel to solve the problem, with clear business and user objectives is necessary. Another important thing is to understand the hardware capabilities. When you start designing the visual, don’t limit yourself to rectangles because in the AR experience users have a complete real-world environment.
Design for MR: Mixed Reality is a great change in the new internet world & designing for Mixed reality is a challenging job for designers. You can consider some UX principles while designing,
- Provide your users with instinctual interactions through hand, eye, and voice inputs,
- Learn how to interact with holograms at close range with a user’s hands or at long range with precise interactions,
- Use voice commands as input in your immersive apps to control surrounding holograms and environments,
- Add a new level of context and human understanding to a holographic experience by using information about what your users are looking at
Conclusion:
According to Gartner, 25% of people will spend at least one hour a day in the metaverse for work, shopping, education, social, and/or entertainment, by 2026.
Today’s new-age customers feel more comfortable interacting and socializing with their peers in the virtual space and the new internet space is offering immersive experiences to people. This new trend has not been fully adopted by the whole world yet, but the pandemic has accelerated its adoption, and industries and users are looking at Web 3.0 as a new opportunity to transact and interact. To remain competitive, designers need to understand, learn, explore and observe more closely this evolving web world to create a better design for today’s users.
About the Author:
Praduman is a self-taught, passionate designer at Mantra Labs’ UI/UX team. His focus is on designing user-friendly interfaces using human-centered principles. Currently he is exploring how the metaverse affects human psychology. He loves to listen to podcasts and read current affairs.
Want to know more about the latest in Blockchain?
Read our blog: Solana: The next in Blockchain
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox