Currently, there are more than 1.73 billion active websites in the world, according to Internet Live Stats. Every second a new website is being created. Creating a website seems simple, but launching a website that serves some specific business purpose is tricky. When business owners approach application/web developers, they encounter jargon like LAMP/MEAN, backend/frontend, DevOps, and many more. In such scenarios, a person not accustomed to web development will either go with his instincts or the developer’s instincts or maybe cost.

To avoid such situations here is an easy-to-understand description of the LAMP stack and MEAN stack along with their best use and related FAQs.
What is LAMP Stack?
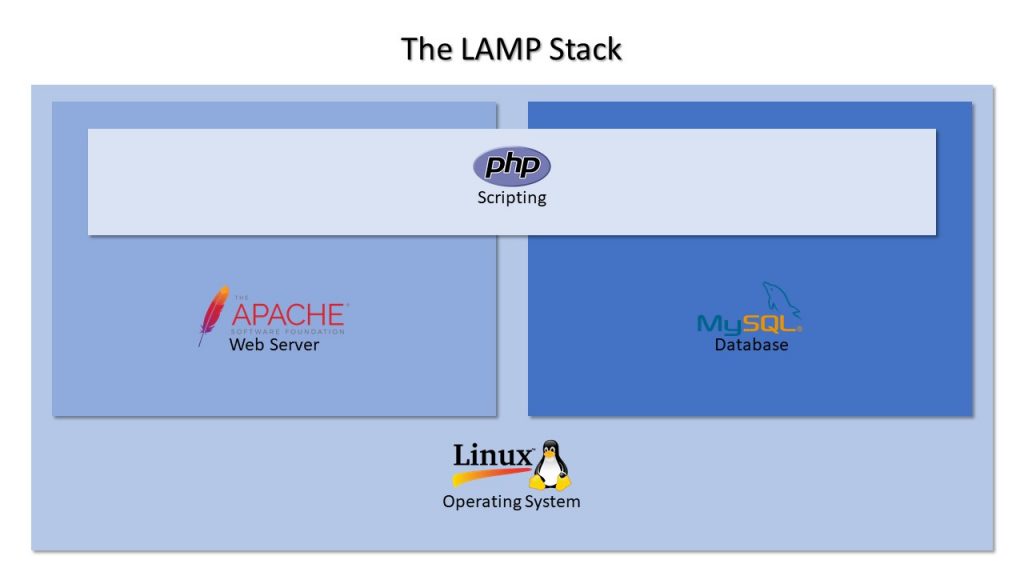
Lamp Stack is a bundle of web development software – Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP. This is the foundational stack where MongoDB and Python can replace MySQL and PHP, respectively.There are four distinct layers under this architecture. Linux is the operating system and all other software applications run on top of this layer. Apache is the web server software responsible for connecting web browsers to the correct website. MySQL is the database to store, retrieve, and update data based on input queries. Finally, PHP is the web programming language. Websites and web applications run on this layer.
What is MEAN Stack?
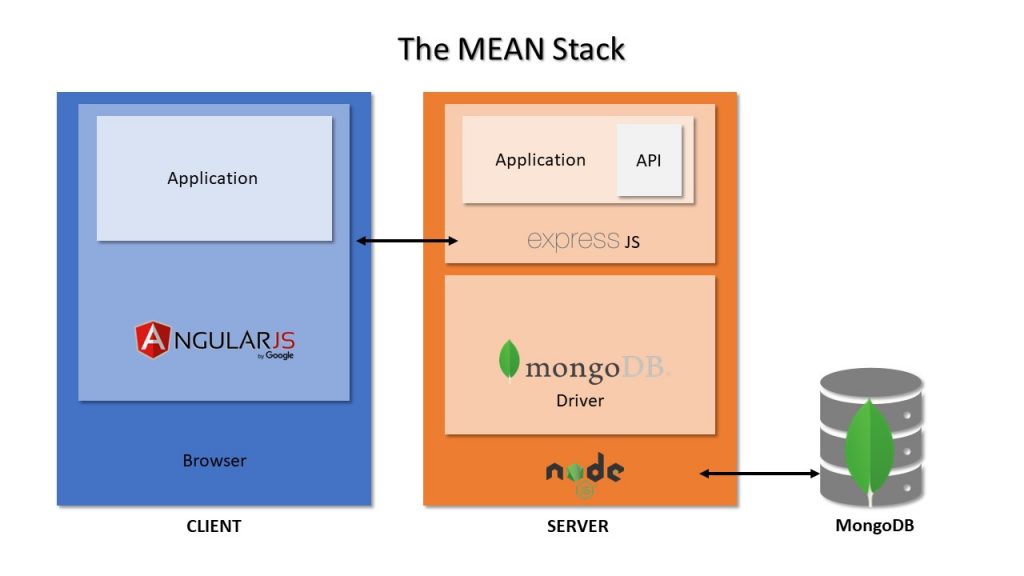
The MEAN stack comprises MongoDB, ExpressJS, AngularJS, and Node.js. It is an open-source javascript-based software stack useful for developing dynamic web applications. Here, JSON (Javascript Object Notation) storage has completely replaced the database layer. JSON is lightweight, easy to understand, and is widely used for storing and transporting data from server to web page.
The components of MEAN Stack-
MongoDB is a NoSQL database system. It is a cross-platform, document-oriented database program. Express is a framework to build web applications in Node. AngularJS provides a framework for frontend development with features like two-way data binding. Node.js provides a server-side javascript execution environment.
LAMP vs MEAN : Which is Better for Startups/Businesses?
LAMP has been in use for decades and many sophisticated applications are built using LAMP stack. MEAN is relatively new, but is considered as one of the best technology stacks for developing mobile applications. However, which one to select totally depends upon the type of web application you want to build.
| LAMP | MEAN | |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | LAMP’s limiting factor is MySQL. During more requests, it creates a bottleneck. I.e. if there is high concurrency, MySQL fails to perform. MySQL works well when there’s a low write/read ratio. | MEAN scales all the layers of frontend, backend, and database. MongoDB supports auto sharding and auto-failover. When the data on one node exceeds the threshold, MongoDB automatically rearranges the data to evenly distribute the data. |
| Performance | Horizontal scaling is not easy and high transaction loads (millions of read/write) seriously affect the performance. | MongoDB is very fast, but it achieves its performance by trading off consistency (in clustered setups). Thus, MongoDB is great when you need speed and flexibility in your model and can accept minor (and relatively infrequent) data loss. |
| Security | LAMP is a secure and stable platform. However, because of different client and server codebases, security is uncompromised in LAMP. | MEAN is a secure and stable platform. |
| Privacy | LAMP applications are mostly native. Therefore, there are negligible privacy issues. | Because of privacy concerns, many users disable javascript on their browser. This might break a MEAN application, since it is completely dependent on Javascript. For example, apps like facebook cannot function properly if the user has disabled the javascript. |
| Development | You might require a full-stack developers team for developing an application on LAMP. For instance, you’ll need a javascript expert for frontend and PHP/Perl/Python expert for the backend. LAMP also features multiple layers of navigation with various configuration files and differing syntax. | A team of javascript experts can develop end-to-end applications on MEAN. |
| Cost | LAMP might cost you more as it requires different specialists for frontend and backend development. | Application development in MEAN is cheaper as you won’t need different specialists.However, the cost depends on the complexity of the project. |
In short, LAMP is best for developing APIs, simple websites, and e-commerce sites. Whereas MEAN is most suitable for Tech-heavy startups, GUI focused Apps and developer teams who are proficient in javascript only.
LAMP/MEAN : What Developers Prefer?
For web applications, there are full-stack developers and MEAN stack developers. Developing an application in LAMP requires a team of developers knowing different frontend and backend technologies and/or full-stack developers. MEAN stack developers require expertise in javascript and because all other components of MEAN are compatible with JS, it is comparatively easier to develop web and mobile applications.
| LAMP | MEAN | |
| Difficulty to learn | LAMP or full-stack developers need to be familiar with all the layers of web development. | MEAN developers require proficiency in programming techniques like javascript and HTML and knowledge of Node.js, Express, MongoDB, and AngularJS. |
| Teams | It can be challenging to switch teams in LAMP. | Using javascript for both frontend and backend development provides a homogenous workflow. Thus, teams can switch from frontend to backend development and vice versa easily. |
| Performance | Developing native applications work well on older browsers and mobile devices. | MEAN applications with javascript heavy frontend might not perform in the second-world countries, where internet speed and devices are not robust. |
| Libraries | LAMP’s library is more mature with a number of functions to make backend development easier. For example, the REST library. | |
| UI | UI-focused apps are easy to build in MEAN and are more intuitive. | |
| Database | You might face scalability concerns with MySQL database. | Although it is fast and capable of dealing with large databases, MongoDB is not the best platform for developing apps with complex transactions. |
Also read – 7 Ways to boost AngularJS applications!
Wrapping Up
MEAN stack mostly includes front end development components while LEAN stack comprises backend tools. You won’t find an operating system reference in MEAN, but, in fact, most MEAN applications are developed on Linux. Thus, we can say — LAMP refers to a more low-level development environment and MEAN to the high-level environment.
It is also possible to modify the technology stacks in both LAMP and MEAN. For instance, you can use MongoDB or Cassandra with other components of LAMP. Some applications can have both stacks — LAMP for the API and MEAN for GUI. Moreover, both software stacks are compatible with the cloud. Therefore, depending on the project you can choose between the two.
We at Mantra Labs frequently encounter the client’s dilemma regarding the choice of LAMP/MEAN stack. Hopefully, this blog clarifies the myths and mysteries encircling these platforms.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




