“We’ve seen more progress in this technology in the last 30 months than we saw in the last 30 years. Ultimately vocal computing is replacing the traditional graphical user interface.” -Shawn DuBravac
Interface design enables humans to experience and interact with technology. Interestingly, Voice User Interface (VUI), is the ability to speak to devices and its capability, in turn, to understand and act upon users’ commands.
Voice user interface: the next-gen of UX
Augmenting human intelligence is a lot more daunting than it looks. The difficulty of mimicking human cognition with software is showing Artificial Intelligence researchers that there’s more than one way to be “intelligent”. The rise of voice can be mainly credited to the evolution of AI and cloud computing capabilities. With machine learning and natural language processing, technology now has the ability to interpret human speech more accurately and in real-time, while also taking note of individual users’ speech tendencies.
This sans-hands method of interaction is rapidly gaining traction. With an approach that is more convenient and human-like, VUI is becoming the next generation of human-computer interaction. From asking Siri to book your appointment with the doc next Monday to asking Alexa to play your favourite show on Amazon Prime; the act of using voice commands has become increasingly natural for users.
At the Google I/O 2018 event, CEO Sundar Pichai demoed Google Duplex: A.I. Assistant calling a local business to make an appointment. The eerily lifelike phone call triggered a wave of intrigue and laughter in the 7,000-strong audience.
Designing a Voice User Interface
Accurate natural language processing has until now existed only in the realm of science fiction. Voice represents the new pinnacle of intuitive interfaces that democratize the use of technology. However tech is still in its nascent stages and not the ultimate incarnation of the medium, but yet it’s currently a strong favourite.
For web and application designers, voice interaction, perhaps, is the biggest UX challenge since the dawn of the touchscreen age. Every voice recognition platform has a unique set of technological constraints. It is essential that you embrace these constraints when architecting a voice interaction UX.
The basic voice UX flow
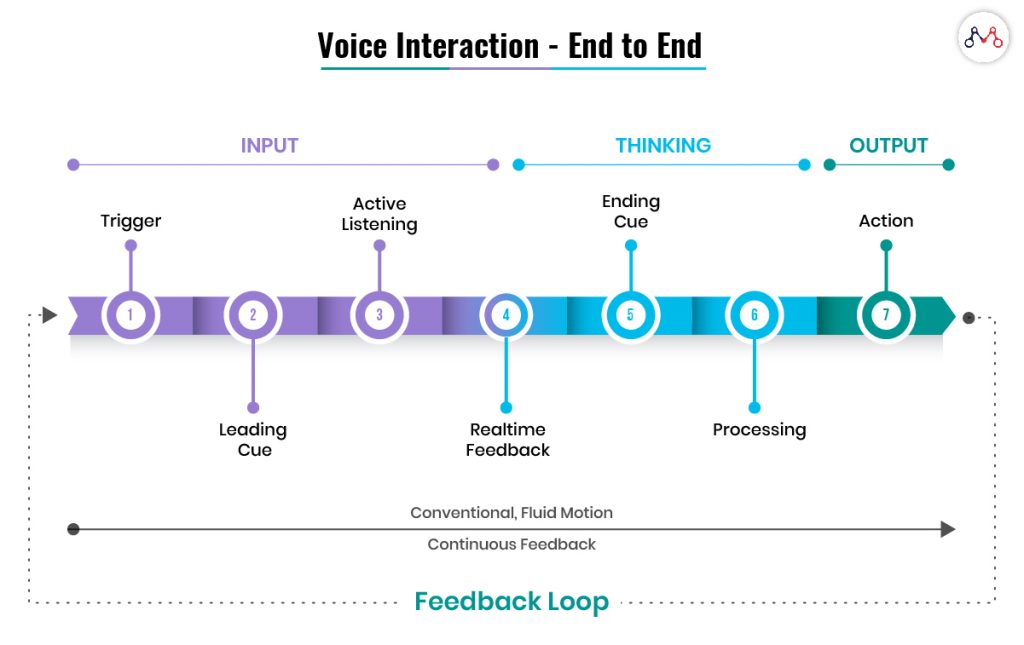
UX was always designed to make interactions as similar to the real world as can be and voice has the potential to make that a reality. UX designers must make sure they’re asking the right questions to elicit the appropriate verbal responses from users. Gender, age, inflexion, tone, accent, cadence and pace are all elements that can be used by UX designers seeking to craft a particular customer experience with their brand.
Below is the sample flow demonstrating the process of speech recognition
A more viable approach could be to prioritize and summarize the information based on known user preferences, prior to delivering an answer – in other words, doing what a normal person would naturally do in a conversation
More complex queries, at times, fall further off the cliff. Risking unpleasant interactions is something brands can rarely afford. Keeping this in mind, error messages could be crafted in a way that’s not only less annoying but also gets users back on track while presenting additional options.
Can we expect a ‘humane’ VUI?
In this age of expected instant gratification, it’s hard to imagine an average user patiently listening to their AI assistant as it narrates a laundry list of all continental restaurants one by one. We want our voice interactions to be as immediate as human alternatives.
VUI’s are extremely complex, multifaceted, and often hybrid amalgams of interaction. Voice interaction may not have garnered the same fanfare just yet. However, for the time being, the creation of a multi-model interface can ignite the furnace for an all-voice controlled interface.
Will VUIs eventually become our primary means of interaction?
Let us know your views by commenting.
Fun fact
Celebrities are likely to find a brand new income stream from licensing not just their voices, but entire personalities as AI assistants. Sounds ridiculous? It does, but you can already pay about $10 to make your TomTom GPS nav unit speak like Snoop Dogg. Go for it!
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




