Today’s Insurance enterprise is moving away from the all-too-familiar ‘reactive-only’ approach to a new predictive-first model. The sector is seeing dramatic changes, as we enter the fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0) — or The Connected Age. Digital businesses are gradually realizing the limitations of human and machine systems without any real intelligence or computing power behind it. Between human prone errors and the scalability challenges of traditional technologies — a new mechanism is required to learn and adapt better.
Enter Cognitive Computing. But what is it?
The short answer is — it has everything to do with interpreting data. Big Data, to be precise. This activity is particularly hard because most of the data in use remains unstructured. In insurance, for example, nearly 90% of carrier data is disparate or partially structured as text & image data, in varying formats. With cognitive computing, data can be made meaningful and then used to derive new insights for future use.
To achieve this, ‘Cognitive Systems’ leverage the use of distinct technologies such as natural language processing, machine learning and automated reasoning. It helps in processing great volumes of complex data and can aid faster & accurate decision-making by breaking down the complexities in big data. When done right, a cognitive computing system can comprehend, reason, learn and interact with humans naturally ultimately enhancing the enterprise’s digital intelligence capabilities.
Another aspect of cognitive computing is the ‘Cloud’ advantage. Cloud computing is not new, however, when fitted with a cognitive solution — it can foster dramatic agility to organizational workflows.
For the digital insurer, this means that all aspects of the value chain can be transformed, ushering in a new business model that seamlessly engages with both customers and prospects in near-real-time, at all times.
Also read – How does XaaS help your business?
The Cognitive Insurance Transformation Journey
Transitioning from a digital to a cognitive business enabled by the ‘cloud’ has a clear business objective behind it — evolve the model to improve profitability. The addition of the cognitive component allows smart systems to free up critical manned resources and drives greater (STP) straight-through processing.
Take ‘underwriting’ for example, which is an area of insurance that necessitates looking at vast heaps of unstructured data. Without the supporting information, the risk cannot be precisely measured or priced.
Accelerating data analysis from historical information can improve the underwriter’s efficiency in the manufacture of meaningful and personalised insurance products, within short turn-around time. This is how insurance carriers will stay their competitive advantage when vying for the wallet-share and mind-share of tomorrow’s customer.
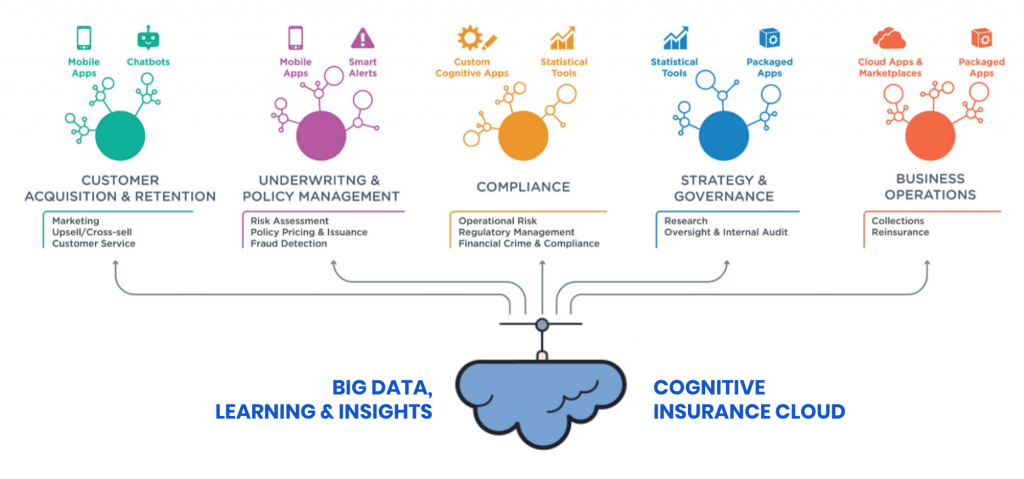
Source: The Cognitive Insurance Value Chain
Yet, the redesign of the underwriting process is only one of many insurance processes that has the potential for Cognitive enhancement. The number of connected things will grow to 25 billion by 2021, which will increase the amount of data. Insurance data alone is expected to grow by 94%. Other parts of the value chain like claims processing, new business and underwriting, rapid customer onboarding, rules-based processes and contract validation are also experiencing cognitive upgradation.
In the past few years, the number of cognitive projects in insurance is on the rise. Carriers are running pilots, testing and validating the right use cases to invest in. For instance, Australian Insurer, Suncorp used IBM’s Watson for ratifying a specific use case — determining who is liable for causing a motor accident, by studying 15,000 historical records of de-personalised claim files.
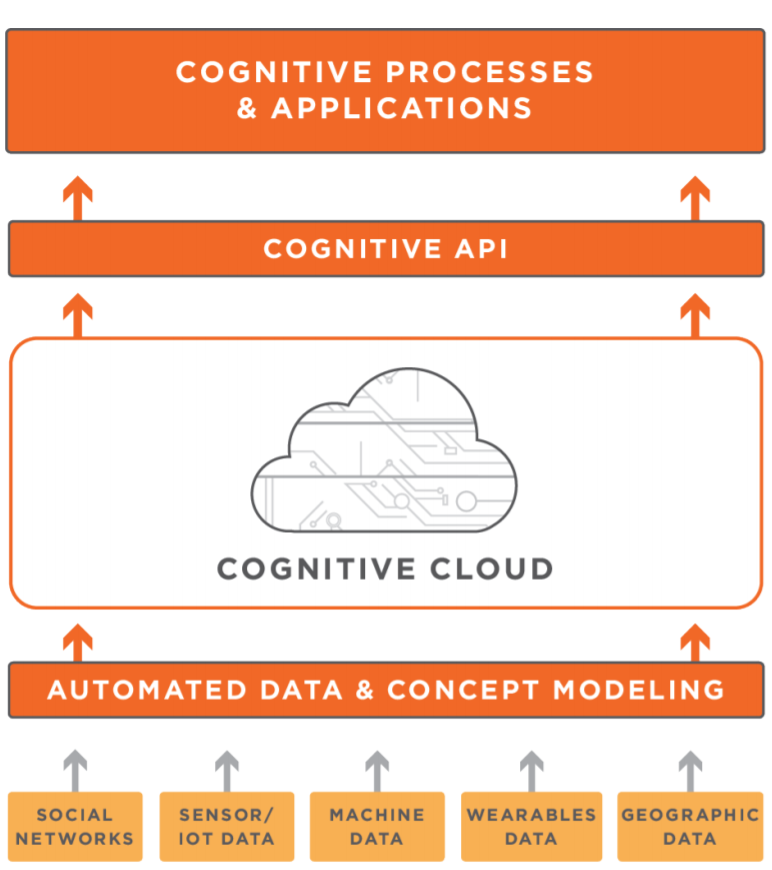
Source: CognitiveScale
Intelligent and cognitive systems like these can do a lot more. From cognitive claims to cognitive chatbots — AI and Machine Learning are behind new behaviour-based, pay-as-you-use products in insurance. Automated post-hospitalisation claims, Motor damage estimation using advanced image recognition, Cognitive mail handling through intention analysis, etc. among others are just a few examples of AI solutions being deployed by Insurers, who are evolving their business models along their transformation journey.
Our own SaaS-based intelligent platform built for improving insurer workflows, FlowMagic takes advantage of cloud-based capabilities to enhance business automation. The intuitive Visual Platform uses AI-powered applications that are easily configurable requiring zero-coding effort, while the jobs can be visually monitored continuously to give real-time decision-ready insights.
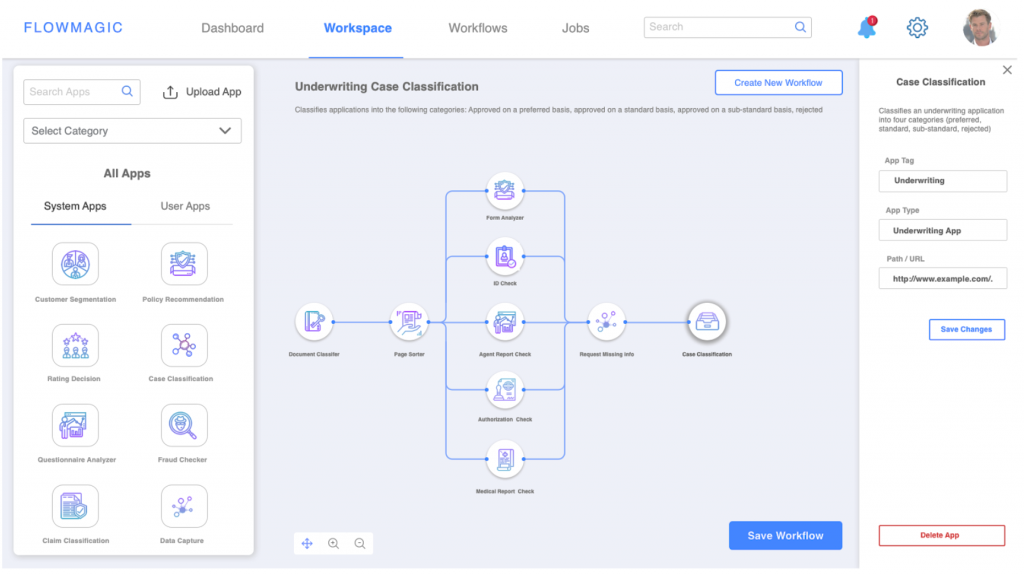
FlowMagic — Visual AI Platform for Insurer Workflows
Here’s a simple 3 step formula for a successful cognitive cloud transformation journey:
1. Identify (internally) use cases with a potential for a high degree of market disruption.
2. Validate (both internally & externally) the use cases through small-scale pilot deployments.
3. Define areas in your operational value chain ripe for transformation, that will enable new processes, engagements and business models through it.
By 2020, 25% of customer service and support operations will integrate with cognitive cloud-enabled chatbots to deliver natural, conversational guidance to users. Solutions like these have proven demonstrable ROI in both front & back-office operations, creating over 80% FTE savings for the enterprise.
Mantra Labs is an InsurTech100 company, that helps digital insurance enterprises enhance agility and operational efficiency through new Cognitive Cloud capabilities. To know how, reach out to us at hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




