Ratemaking, or insurance pricing, is the process of fixing the rates or premiums that insurers charge for their policies. In insurance parlance, a unit of insurance represents a certain monetary value of coverage. Insurance companies usually base these on risk factors such as gender, age, etc. The Rate is simply the price per ‘unit of insurance’ for each unit exposed to liability.
Typically, a unit of insurance (both in life and non-life) is equal to $1,000 worth of liability coverage. By that token, for 200 units of insurance purchased the liability coverage is $200,000. This value is the insurance ‘premium’. (This example is only to demonstrate the logic behind units of exposure, and is not an exact method for calculating premium value)
The cost of providing insurance coverage is actually unknown, which is why insurance rates are based on the predictions of future risk.
Actuaries work wherever risk is present
Actuarial skills help measure the probability and risk of future events by understanding the past. They accomplish this by using probability theory, statistical analysis, and financial mathematics to predict future financial scenarios.
Insurers rely on them, among other reasons, to determine the ‘gross premium’ value to collect from the customer that includes the premium amount (described earlier), a charge for covering losses and expenses (a fixture of any business) and a small margin of profit (to stay competitive). But insurers are also subject to regulations that limit how much they can actually charge customers. Being highly skilled in maths and statistics the actuary’s role is to determine the lowest possible premium that satisfies both the business and regulatory objectives.
Risk-Uncertainty Continuum
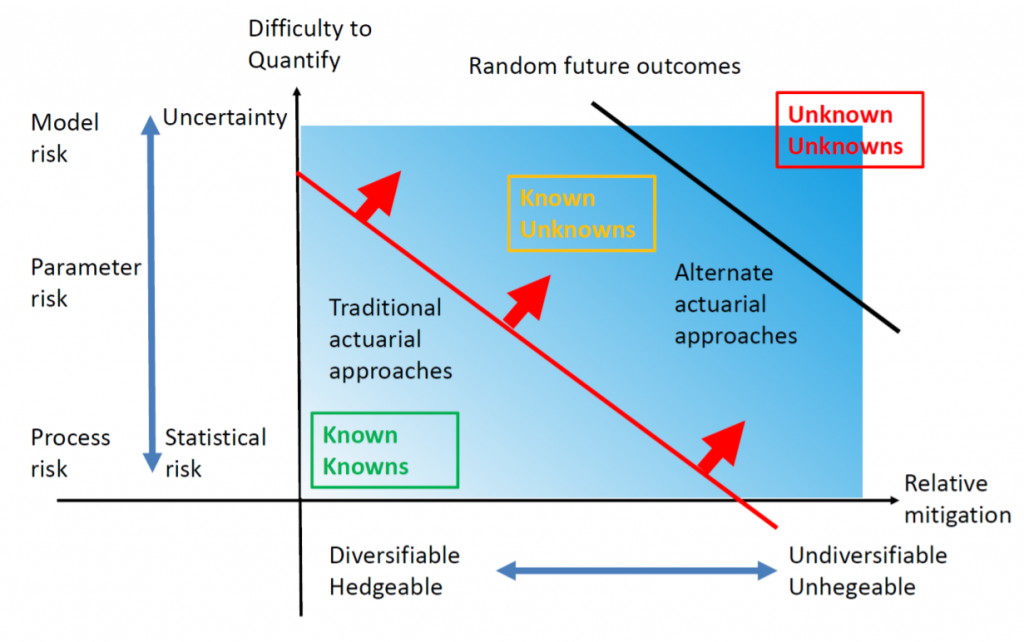
Source: Sam Gutterman, IAA Risk Book
Actuaries are essentially experts at managing risk, and owing to the fact that there are fewer actuaries in the World than most other professions — they are highly in demand. They lend their expertise to insurance, reinsurance, actuarial consultancies, investment, banking, regulatory bodies, rating agencies and government agencies. They are often attributed to the middle office, although it is not uncommon to find active roles in both the ‘front and middle’ office.
Recently, they have also found greater roles in fast growing Internet startups and Big-Tech companies that are entering the insurance space. Take Gus Fuldner for instance, head of insurance at Uber and a highly sought after risk expert, who has a four-member actuarial team that is helping the company address new risks that are shaping their digital agenda. In fact, Uber believes in using actuaries with data science and predictive modelling skills to identify solutions for location tracking, driver monitoring, safety features, price determination, selfie-test for drivers to discourage account sharing, etc., among others.
Also read – Are Predictive Journeys moving beyond the hype?
Within the General Actuarial practice of Insurance there are 3 main disciplines — Pricing, Reserving and Capital. Pricing is prospective in nature, and it requires using statistical modelling to predict certain outcomes such as how much claims the insurer will have to pay. Reserving is perhaps more retrospective in nature, and involves applying statistical techniques for identifying how much money should be set aside for certain liabilities like claims. Capital actuaries, on the other hand, assess the valuation, solvency and future capital requirements of the insurance business.
New Product Development in Insurance
Insurance companies often respond to a growing market need or a potential technological disruptor when deciding new products/ tweaking old ones. They may be trying to address a certain business problem or planning new revenue streams for the organization. Typically, new products are built with the customer in mind. The more ‘benefit-rich’ it is, the easier it is to push on to the customer.
Normally, a group of business owners will first identify a broader business objective, let’s say — providing fire insurance protection for sub-urban, residential homeowners in North California. This may be a class of products that the insurer wants to open. In order to create this new product, they may want to study the market more carefully to understand what the risks involved are; if the product is beneficial to the target demographic, is profitable to the insurer, what is the expected value of claims, what insurance premium to collect, etc.
There are many forces external to the insurance company — economic trends, the agendas of independent agents, the activities of competitors, and the expectations and price sensitivity of the insurance market — which directly affect the premium volume and profitability of the product.
Dynamic Factors Influencing New Product Development in Insurance
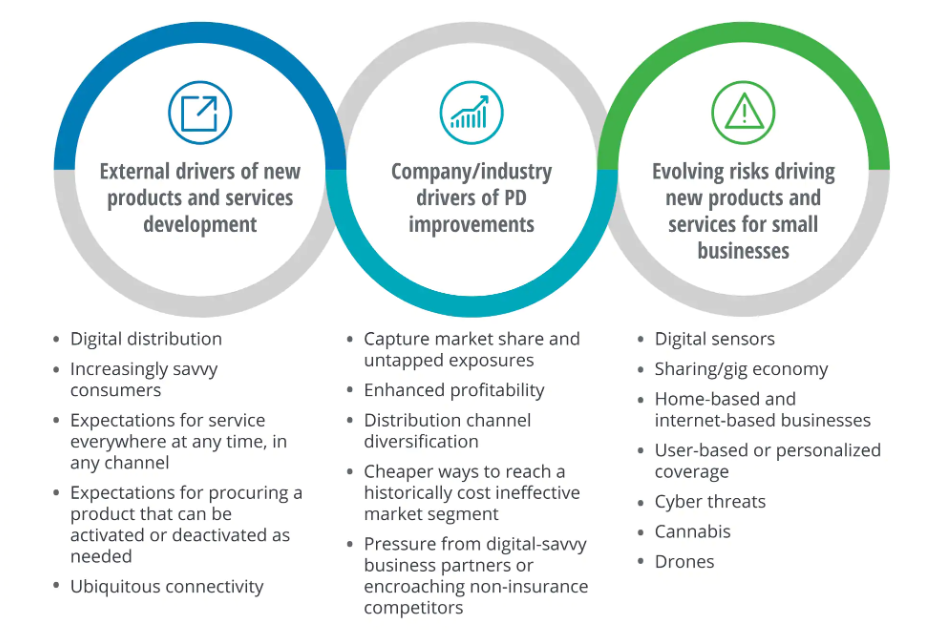
Source: Deloitte Insights
To determine insurance rate levels and equitable rating plans, ratemaking becomes essential. Statistical & forecasting models are created to analyze historical premiums, claims, demographic changes, property valuations, zonal structuring, and regulatory forces. Generalized linear models, clustering, classification, and regression trees are some examples of modeling techniques used to study high volumes of past data.
Based on these models, an actuary can predict loss ratios on a sample population that represents the insurer’s target audience. With this information, cash flows can be projected on the product. The insurance rate can also be calculated that will cover all future loss costs, contingency loads, and profits required to sustain an insurance product. Ultimately, the actuary will try to build a high level of confidence in the likelihood of a loss occurring.
This blog is a two-part series on new product development in insurance. In the next part, we will take a more focused view of the product development actuary’s role in creating new insurance products.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




