The concept of ‘smart contract’ was introduced by Nick Szabo, an American cryptographer and computer scientist in 1994. But, only after blockchain became widespread in 2008, people understood practical applications of smart contracts.
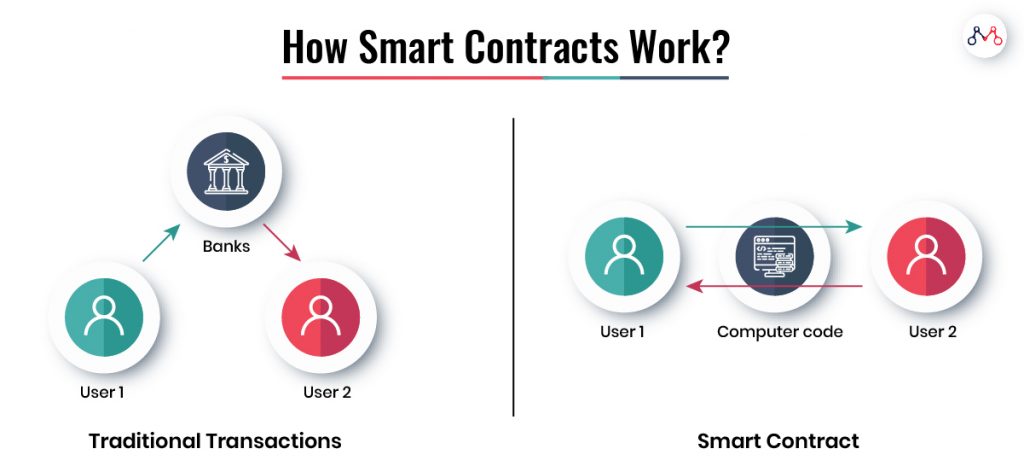
A smart contract is a computer protocol (set of rules) that digitally facilitates, verifies, and enforces the negotiations between two parties. It uses a distributed ledger system (blockchain) to store data on public databases and perform transactions without involving third parties.
In this article, we’ll discuss the legal aspects of smart contracts in India. Before we do, here is a brief insight into how smart contracts work.
How Are Smart Contracts Executed?
The smart contract is a blockchain-based computer code. The contract terms are written in the code itself. Smart contracts interpret and verify every transaction against the terms and automatically executes them.
The key features of smart contracts are-
- Once the smart contract is released, no one including the creator (owner) can modify its terms.
- Physical documents are not required to initiate and complete the transaction.
- Although users can remain anonymous, the smart contract records the transaction details.
- Moderators can track market activity, but cannot regulate the transactions.
- Smart contract transactions are irreversible.
Smart Contract Real Estate Use Case: Propy
For instance, Propy is a smart contract-based cross-continental marketplace for buying and selling properties. It allows owners and brokers to list their properties and allows sellers to search and negotiate irrespective of location. The deal is closed through online transactions and each deed is recorded in the blockchain.
Viability of Smart Contracts in India?
Indian jurisdiction does not allow its financial institution to undertake bitcoin transactions. Since bitcoins demonstrate peer-to-peer transactional network, the fact that it is forbidden questions the viability of “Smart Contract” in India.
However, section 10 of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 states – “All agreements are contracts if they are made by the free consent of parties competent to contract, for a lawful consideration and with a lawful object, and are not hereby expressly declared to be void.”
Therefore, legally, two parties can sign a contract with or without third party involvement. By definition, the Indian Contract Act 1872 allows Smart Contracts.
Also, sections 5 and 10 of the Indian Information Technology Act, 2000 legally recognize digital signatures and considers a contract formed through electronic means as valid and enforceable.
Despite Indian law allowing for digital contracts, Ponzi schemes facilitated by blockchain questions the viability of technology to safeguard people’s interests. Amit Bhardwaj’s $300 Mn cryptocurrency fraud calls for a strict ordinance for peer-to-peer contracts.
Since Smart Contracts do not involve a regulatory third party, fraud-control is a real concern. But, according to section 65B of the Indian Evidence Act, 1872 digitally signed contracts are admissible in a court of law. Therefore, the government can intervene to resolve the disputes between participants. Also, sections 17, 18, and 19 of the Indian IT Act, 2000 allows supervision from national and foreign governing authorities.
Drop us a ‘hi’ at hello@mantralabsglobal.com to learn more about building industry-specific smart contracts and products.
Smart Contracts Insurance Use Case: Fizzy
AXA’s Fizzy is a smart contract-based travel insurance scheme for flight delays and cancellations. It ensures transparency as the claims displayed on the website are stored in a blockchain and no one can change the terms after purchase.
User can buy the insurance online. When the flight is delayed or canceled, the public databases of plane status information automatically triggers the insurance holder’s compensation. The event confirmation executes and closes the claim process instantly.
Are There Business Benefits From Smart Contracts?
Almost all businesses (viz. Insurance, automobile, healthcare, supply chain, real estate, education, etc.) can benefit from smart contract development.
Transparency and data immutability are the competitive advantages that Smart Contracts bring to users on a global scale. With accurate record-keeping, companies can overcome fraud and business inconsistencies. Especially pay-per-use and micro-transactions can save paperwork and costs associated. For instance, insurers can manage micro insurances better through smart contracts than traditional models.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




