SQL Query optimization is a process of writing thoughtful SQL queries to improve database performance. During development, the amount of data accessed and tested is less. Hence, developers get a quick response to the queries they write. But the problem starts when the project goes live and enormous data starts flooding the database. Such instances slow down SQL queries response drastically and create performance issues.
When working with large-scale data, even the most minor change can have a dramatic impact on performance.
SQL performance tuning can be an incredibly difficult task. Even a minor change can have a dramatic impact on performance. Here are the 10 most effective ways to optimize your SQL queries.
- Indexing: Ensure proper indexing for quick access to the database.
- Select query: Specify the columns in SELECT query instead of SELECT* to avoid extra fetching load on the database.
- Running queries: Loops in query structure slows the sequence. Thus, avoid them.
- Matching records: Use EXITS() for matching if the record exists.
- Subqueries: Avoid correlated sub queries as it searches row by row, impacting the speed of SQL query processing.
- Wildcards: Use wildcards (e.g. %xx%) wisely as they search the entire database for matching results.
- Operators: Avoid using function at RHS of the operator.
- Fetching data: Always fetch limited data.
- Loading: Use a temporary table to handle bulk data.
- Selecting Rows: Use the clause WHERE instead of HAVING for primary filters.
SQL Query Optimization Tips with Examples
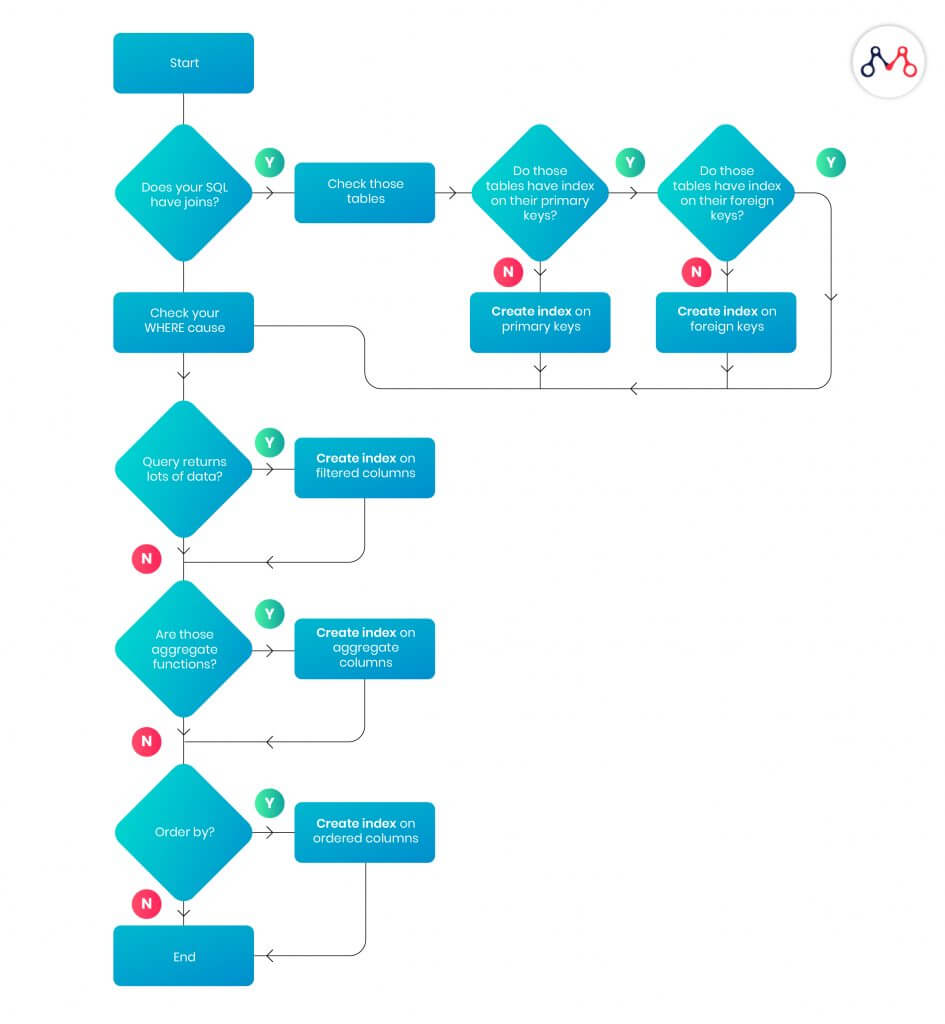
Tip 1: Proper Indexing
An index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table. A unique index creates separate data columns without overlapping each other. Proper indexing ensures quicker access to the database, i.e. you’ll be able to select or sort rows faster. The following diagram explains the basics of indexing while structuring tables.
TIP 2: Use SELECT <columns> instead of SELECT *
Specify the columns in the SELECT clause instead of using SELECT *. The unnecessary columns place extra load on the database, which slows down not just the single SQL, but the whole system.
Inefficient
SELECT * FROM employees
This query fetches all the data stored in the “employees” table such as phone number, activity dates, notes from sales, etc. which might not be required for a particular scenario.
Efficient
SELECT first_name, last_name, mobile, city, state FROM employees
This query will fetch only selected columns.
Tip 3: Avoid running queries in a loop
Coding SQL queries in loops slows down the entire sequence. Instead of writing a query that runs in a loop, you can use bulk insert and update depending on the situation. Suppose there are 1000 records. Here, the query will execute 1000 times.
Inefficient
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
$query = “INSERT INTO TBL (A,B,C) VALUES . . . .”;
$mysqli->query($query);
printf (“New Record has id %d.\ “, $mysqli->insert_id);
}
Efficient
INSERT INTO TBL (A,B,C) VALUES (1,2,3), (4,5,6). . . .
Tip 4: Does My record exists?
Normally, developers use EXITS() or COUNT() queries for matching a record entry. However, EXIT() is more efficient as it will exit as soon as finding a matching record; whereas, COUNT() will scan the entire table even if the record is found in the first row.
Inefficient
IF (SELECT COUNT(1) FROM EMPLOYEES WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE ‘%JOHN%’) > 0 PRINT ‘YES’
Efficient
IF EXISTS(SELECT FIRSTNAME FROM EMPLOYEES WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE ‘%JOHN%’)
PRINT ‘YES’
Tip 5: A big NO for correlated subqueries
A correlated subquery depends on the parent or outer query. Since it executes row by row, it decreases the overall speed of the process.
Inefficient
SELECT c.Name, c.City,(SELECT CompanyName FROM Company WHERE ID = c.CompanyID) AS CompanyName FROM Customer c
Here, the problem is — the inner query is run for each row returned by the outer query. Going over the “company” table again and again for every row processed by the outer query creates process overhead. Instead, for SQL query optimization, use JOIN to solve such problems.
Efficient
SELECT c.Name, c.City, co.CompanyName FROM Customer c LEFT JOIN Company co ON c.CompanyID = co.CompanyID
Tip 6: Use wildcard characters wisely
Wildcard characters can be either used as a prefix or a suffix. Using leading wildcard (%) in combination with an ending wildcard will search all records for a match anywhere within the selected field.
Inefficient
Select name from employees where name like ‘%avi%’
This query will pull the expected results of Avishek, Avinash, Avik and so on . However, it will also pull unexpected results, such as David, Xavier, Davin.
Efficient
Select name from employees where name like ‘avi%’.
This query will pull only the expected results of Avishek, Avinash, Avik and so on.
Tip 7: Avoid using SQL function on the RHS of the operator
Often developers use functions or methods with their SQL queries.
Inefficient
Select * from Customer where YEAR(AccountCreatedOn) == 2005 and MONTH(AccountCreatedOn) = 6
Note that even though AccountCreatedOn has an index, the above query changes the WHERE clause in such a way that this index cannot be used anymore.
Efficient
Select * From Customer Where AccountCreatedOn between ‘6/1/2005’ and ‘6/30/2005’
Tip 8: Always fetch limited data and target accurate results
Lesser the data retrieved, the faster the query will run. Rather than applying too many filters on the client-side, filter the data as much as possible at the server. This limits the data being sent on the wire and you’ll be able to see the results much faster.
Tip 9: Drop index before loading bulk data
If you want to insert thousands of rows in an online system, use a temporary table to load data. Ensure that this temporary table does not have any index. Since moving data from one table to another is much faster than loading them from an external source; you can now drop indexes on your primary table, move data from temporary to the final table, and finally recreate the indexes.
Tip 10: Use WHERE instead of HAVING
HAVING clause filters the rows after all the rows are selected. It is just like a filter. Do not use the HAVING clause for any other purposes.
In the SQL Order of Operations, HAVING statements are calculated after WHERE statements. Therefore, executing the WHERE query is faster.
Hope you enjoyed reading these tips for SQL query optimization. If you have any questions, feel free to drop a comment or write to us at hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
You can learn more about SQL queries and syntax at W3Schools tutorial.
About Author: Avishek Kumar Singh is a Senior Tech Lead at Mantra Labs — a leading application development service provider in insurtech and e-commerce domains. He has years of experience in developing robust web and mobile applications for enterprises.
Suggest reading – LAMP/MEAN Stack: Business and Developer Perspective
Common FAQs
SQL optimization is a process of using SQL queries in the best possible way to get accurate and fast database results. The most common database queries are INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and CALL. These are coupled with subqueries to filter the results. This is where people need to think of optimization to get accurate results with fewer resources and improve database performance.
SQL optimization is also known as SQL query tuning. Basically, it is a process of smartly using SQL queries to increase the speed of fetching data and improve overall database performance.
There are two most common query optimization techniques – cost-based optimization and rule (logic) based optimization. For large databases, a cost-based query optimization technique is useful as it table join methods to deliver the required output. Rule-based optimization combines two or more queries based on relational expressions. The following example illustrates rule-based query optimization.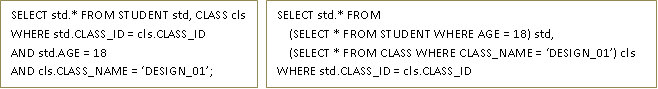
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




