We need to test websites and applications for performance standards before delivering them to the client. The performance or benchmark testing is an ongoing function of software quality assurance that extends throughout the life cycle of the project. To build standards into the architecture of a system — the stability and response time of an application is extensively tested by applying a load or stress to the system.
Essentially, ‘load’ means the number of users using the application while ‘stability’ refers to the system’s ability to withstand the load created by the intended number of users. ‘Response time’ indicates the time taken to send a request, run the program and receive a response from a server.
Load testing on applications can be a challenging ordeal if a performance testing strategy is not predetermined. Testing tasks require multifaceted skill-sets — from writing test scripts, monitoring and analyzing test results to tweaking custom codes and scripts, and developing automated test scenarios for the actual testing.
So, is load testing on applications really necessary?
Quality testing ensures that the system is reliable, built for capacity and scalable. To achieve this, the involved stakeholders decide the budget considering its business impact.
Now, this raises a question — how do we predict traffic based on past trends? and how can we make the system more efficient to handle traffic without any dropouts? Also, if and when we hit peak loads, then how are we going to address the additional volume? For this, it is crucial to outline the performance testing strategy beforehand.
5 Key Benefits of Performance Testing
- It identifies the issues at the early stage before they become too costly to resolve (for example, exposing bugs that do not surface in cursory testing, such as memory management bugs, memory leaks, buffer overflows, etc.).
- Performance testing reduces development cycles, produces better quality and more scalable code.
- It prevents revenue and credibility loss due to poor web site performance.
- To enable intelligent planning for future scaling.
- It ensures that the system meets performance expectations (response time, throughput, etc.) under-designed levels of load.
Organizations don’t prefer manual testing these days because it is expensive and requires human resources and hardware. It is also quite complex to coordinate and synchronize multiple testers. Also, repeatability is limited in manual testing.
To find the stability and response time of each API, we can test different scenarios by varying the load at different time intervals on the application. We can then automate the application by using any performance testing tool.
Performance Testing Tools
There are a bunch of different tools available for testers such as Open Source testing Tools — Open STA Diesel Test, TestMaker, Grinder, LoadSim, J-Meter, Rubis; Commercial testing tools— LoadRunner, Silk Performer, Qengine, Empirix e-Load.
Among these, the most commonly used tool is Apache J-Meter. It is a 100% Java desktop application with a graphical interface that uses the Swing graphical API. It can, therefore, run on any environment/workstation that accepts Java virtual machine, for example, Windows, Linux, Mac, etc.
We can automate testing the application by integrating the ‘selenium scripts’ in the J-Meter tool. (The software that can perform load tests, performance-functional tests, regression tests, etc. on different technologies.)
[Related: A Complete Guide to Regression Testing in Agile]
If the project is large in scope and the number of users keeps increasing day-by-day then the server’s load will be greater. In such situations, Performance testing is useful to identify at what point the application will crash. To find the number of errors and warnings in the code, we use the J-Meter tool.
How J-Meter Works
J-Meter simulates a group of users sending requests to a target server and returns statistics that show the performance/functionality of the target server/application via tables, graphs, etc.
The following figure illustrates how J-Meter works:
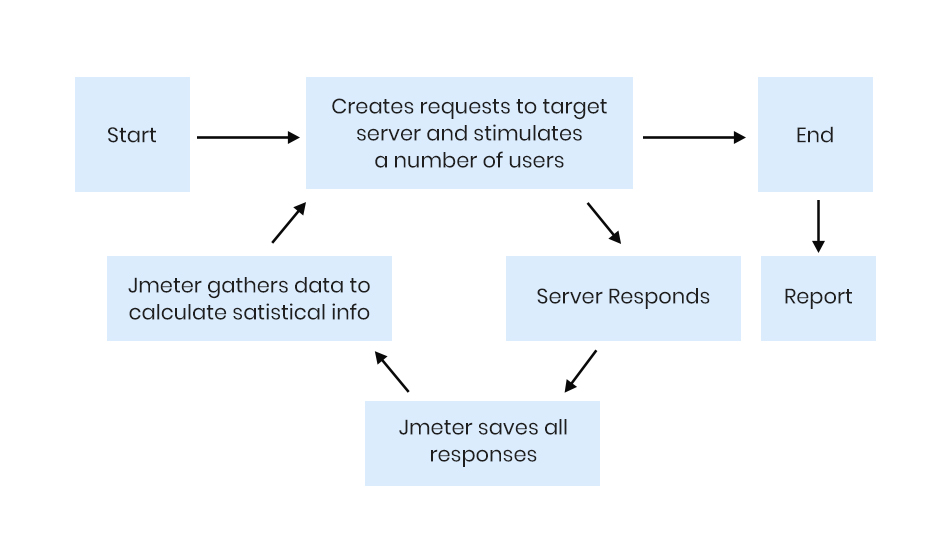
The J-Meter performance testing tool can find the performance of any application (no matter whatever the language used to build the project).
First, it requires a test plan which describes a series of steps that the J-Meter will execute when run. A complete test plan will consist of one or more thread groups, samplers, logic controllers, listeners, timers, assertions and configuration elements.
The ‘thread’ group elements are the beginning of any test plan. Thread group element controls the number of threads J-Meter will use during the test run. We can also control the following via thread group: setting the number of threads, setting the ramp-up time and setting the loop count. The number of threads implies the number of users to the server application, while the ramp-up period defines the time taken by J-Meter to get all the threads running. Loop count identifies the number of times to execute the test.
After creating the ‘thread’ group, we need to define the number of users, iterations and ramp-up time (or usage time). We can create virtual servers depending on the number of users defined in the thread group and start performing the action based on the parameters defined. Internally J-Meter will record all the results like response code, response time, throughput, latency, etc. It produces the results in the form of graphs, trees and tables.
J-Meter has two types of controllers: Samplers and Logic controllers. Samplers allow the J-Meter to send specific requests to a server, while Logic controllers control the order of processing of samplers in a thread. They can change the order of requests coming from any of their child elements. Listeners are then used to view the results of samplers in the form of reporting tables, graphs, trees or simple text in some log files.
Please remember, always do performance testing by changing one parameter at a time. This way, you’ll be able to monitor response and throughput metrics and correct discrepancies accordingly. The real purpose of load testing is to ensure that the application or site is functional for businesses to deliver real value to their users — so test practically, and think like a real user.
If you’ve any queries or doubts, please feel free to write to hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
About the author: Syed Khalid Hussain is a Software Engineer-QA at Mantra Labs Pvt Ltd. He is a pro at different QA testing methodologies and is integral to the organization’s testing services.
Load Testing on Applications FAQs
Load testing is done to ensure that the application is capable of withstanding the load created by the intended number of users (web traffic).
There are open source and commercial tools available for load testing.
Open Source Tools are — Open STA Diesel Test, TestMaker, Grinder, LoadSim, J-Meter, Rubis. Commercial testing tools are — LoadRunner, Silk Performer, Qengine, Empirix e-Load.
Load testing is done using test scripts, monitoring and analyzing test results and developing automated test scenarios.
Check out these articles to catch the latest trends in mobile apps:
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox





