To scale-up the employee and customer satisfaction levels, enterprises frequently roll features to their software and applications. For instance, ING — the Dutch multinational financial services company releases features to its web and mobile sites every three weeks and has reported impressive improvement in its customer satisfaction scores.
New releases and enhancements are integral to agile businesses. But with these, comes the requirement to ensure a seamless experience for the user while using the application.
Whenever there is a change in code across multiple releases or multiple builds for the enhancement or bug fix and due to these changes there might be an Impact Area. Testing these Impact Areas is known as Regression Testing.
Regression Testing Cases
Regression testing is a combination of all the functional, integration and system test cases. Here, testers pick the test cases from the Test Case Repository. Organizations use regression testing in the following ways-
- Executing the old test cases for the next release for any new feature addition.
- Only after passing new test cases, the system executes the old test cases of the previous release.
Mainly, regression testing requires 3 things-
- Addition of new test cases in the test case repository.
- Deletion or retiring of the old test cases which have no relation to any module of an application.
- Modification of the old test cases with respect to enhancement or changes in the existing features.
Types of Regression Testing
There are 3 main types of regression testing in agile:
1. Unit Regression Testing
This testing method tests the code as a single unit.
- It tests the changed unit only.
- If there’s a minor code change, testing is done on that particular module and all the components which have dependencies between them.
- Here, testers need not find the impact area.
- It is possible to modify or re-write existing test cases.
2. Regional Regression Testing
It involves testing the Impacted Areas of the software due to new feature releases or major enhancement to the existing features.
- It involves testing the changing unit and the Impact Area.
- Regional regression testing requires rewriting the entire test cases as it corresponds to a major change.
- It requires deleting the old test case and adding a new test case to the repository.
- It may affect other dependent features. Therefore, it requires identifying the Impact Areas and picking up old test cases from the test case repository and test the dependent modules referring to the old test cases.
3. Full Regression Testing
It is a comprehensive testing method that involves testing the changed unit as well as independent old features of the application.
- Here, the changed unit, as well as the complete application (independent or dependent), is tested.
- Full regression testing is mostly applicable for LIFE CRITICAL or MACHINE CRITICAL Applications.
Regression testing is also done at the product/application development stage.
4. Release Level Regression Testing
Regression testing at release level corresponds to testing during the second release of an application.
- It always starts from the second release of an application.
- Usually, when organizations seek to add new features or enhancing existing features of an application a new release needs to go live, for which, this type of regression testing is done.
- Release level regression testing refers to testing on the Impact Area and involves finding out the regression test case accordingly.
5. Build Level Regression Testing
Regression testing at build level corresponds to testing during the second build of the upcoming release.
- It takes place whenever there’s some code changes or bug fixes across the builds.
- QA first retest the bug fixes and then the impact area.
- This cycle of build continues until a final stable build.
- The final stable build is given to the customer or when the product is live.
- QA is usually aware of the product and utilizes their Product knowledge to identify the impact areas.
The Process of Regression Testing in Agile
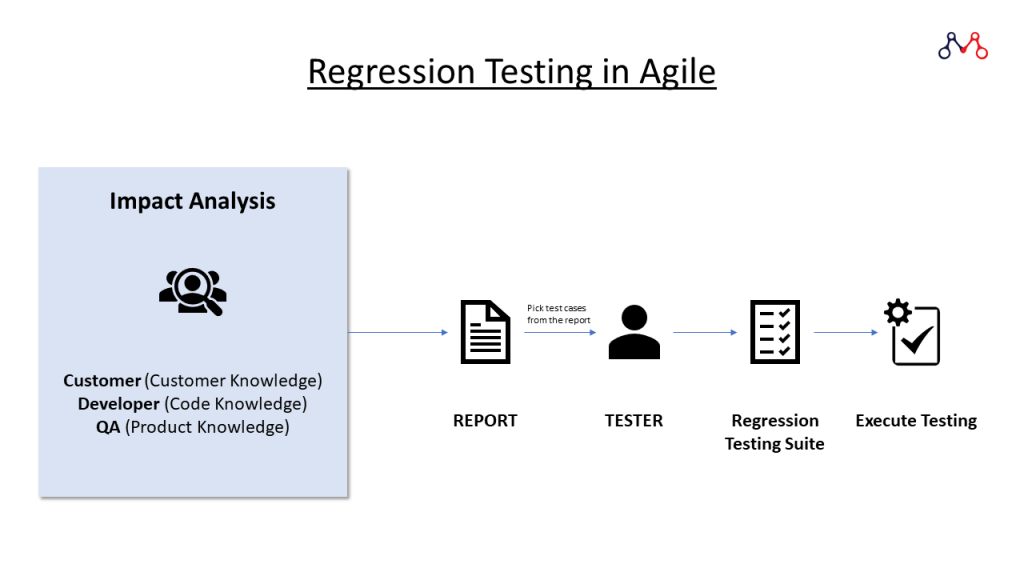
- After getting the requirements and understanding it completely, testers perform Impact Analysis to find the Impact Areas.
- One should perform regression testing when the new features are stable.
- To avoid major risks it is better to perform Impact Analysis in the beginning.
- 3 stakeholders can carry out Impact Analysis:
- Customers based on Customer Knowledge.
- Developer based on Coding Knowledge.
- And, most importantly by the QA based on the Product Knowledge.
- All three stakeholders make their reports and the process continues till achieving the maximum impact area.
- Then the Team Lead consolidates all the reports and picks test cases from the test case repository to prepare Regression Testing Suite for QA Engineers. Post this, the final execution process starts.
The main challenges of Regression Testing is to Identify the Impact Area.
Challenges of Manual Regression Testing
- Time-Consuming as the test cases increase release by release.
- The need for more manual QA Engineers.
- Repetitive and monotonous tasks; therefore accuracy is always a question.
This is where Test Automation comes into place.
Advantages of Test Automation
- Time-saving: Test Automation executes test cases in batches making it faster. I.e. it is possible to execute multiple test cases simultaneously.
- Reusability: It allows reusing the test script in the next release when the impact areas are the same.
- Cost-effective: There’s no need for additional resources for executing similar test cases again and again.
- Accurate: Machine-based procedures are not prone to slip errors.
Read more: Everything about Test Automation as a Service (TAAAS)
It may look like Test Automation might replace manual QA Engineers, but that’s not the case. Regression testing in agile still requires QA in the following instances.
Limitations of Test Automation
- It is not possible to automate testing for new features. Test Automation Engineers still need to write test scripts.
- Similarly, it’s not possible to automate testing in case of a feature update.
- There is no technology support such as Captcha.
- It requires human involvement; such as OTP.
- At times, certain test cases require more time in test automation. During such instances, one can go for manual testing. For example, 5 Test Cases require 1 hour to execute it manually whereas Test Automation takes a complete 5 hours executing it.
In agile, enterprises need testing with each sprint. On the other hand, testers need to ensure that new changes do not affect existing functionalities of the product/application. Therefore, agile combines both regression testing and test automation to accelerate the product’s time-to-market.
If you’re looking for Testing Services for your Enterprises, please feel free to drop us a word at hello@mantralabsglobal.com. You can also check out our Testing Services.
Quality is never an accident; it is always the result of intelligent effort.
John Ruskin
About the author: Ankur Vishwakarma is a Software Engineer — QA at Mantra Labs Pvt Ltd. He is integral to the organization’s testing services. Apart from writing test scripts, you can find Ankur hauling on his Enfield!
Regression Testing FAQs
Regression testing is done to ensure that any new feature or enhancement in the existing application runs smoothly and any change in code does not impact the functionality of the product.
UAT corresponds to User Acceptance Testing. It is the last phase of the software testing process. Regression Testing is not a part of UAT as it is done on product/application features and updates.
Agile implies an iterative development methodology. Agile testing corresponds to a continuous process rather than sequential. In this method, features are tested as they’re developed.
Functional testing ensures that all the functionalities of an application are working fine. It is done before the product release. Regression testing ensures that new features or enhancements are working correctly after the build is released.
Related:
- Test Automation Services
- Modern Medical Enterprises Absolutely Need Test Automation. Here’s Why.
- Medical Image Management: DICOM Images Sharing Process
- Basics of load testing in Enterprise Applications using J-Meter
- [Part 1] Web Application Security Testing: Top 10 Risks & Solutions
- [Part 2] Web Application Security Testing: Top 10 Risks & Solutions
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




