For modern healthcare organizations, extending better patient care across the service continuum involves new challenges that surround sharing information over a distributed network. Effectively sharing patient information remains a challenge. However, the inability to access these records in a time-sensitive manner results in re-imaging and re-testing the patients. It affects both — ‘time-to-treatment’ and the bottom line. Effective medical image management thus becomes crucial for every digital healthcare enterprise.
The release process for medical images is altogether complicated — brimming with security related-risks. Images (such as X-Ray Scans, MRI scans, PET scans, etc.) are created and released across several departments and systems while being purposefully kept ‘out-of-reach’ from a host of unauthorized users.
Training & controls on release policies and procedures require ‘health information management’ expertise. It’s because image Handling (electronically) can become susceptible to data corruption, complex accessibility/sharing issues and high-security risks. All of these raise potential red flags for health information management (HIM) professionals.
So how does Medical Image sharing work in this environment? What, if any — are the safeguards surrounding the ‘release’ process?
Medical Image Management: Sharing DICOM Images across healthcare enterprises
Before we go further, let’s delve into the term ‘Medical Imaging’. According to the WHO, the technique embodies different imaging modalities and processes to image the human body (creating visual representations) for diagnostic and treatment purposes. — making it crucial for improving public health initiatives across all population groups.
First, the image is captured using a medical imaging device (routine imaging techniques like ultrasound, MRI, etc.). Then it is necessary to archive and store the images for future use and further processing. Unlike regular images (.png, .jpeg), medical images use DICOM format for storage. DICOM is Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine standard. The medical practitioner responsible for acquiring and interpreting such medical images is a ‘Radiologist’. And the system they rely on for storing electronic image data is ‘PACS’ (Picture Archiving and Communication System).
If a healthcare organization or an outside consultant (physician, clinician) needs access to an individual patient’s medical images, then the access and retrieval will have to go through PACS. Typically, a Radiologist has authority to control and operate PACS.
Here is a simple process diagram of a medical imaging system —
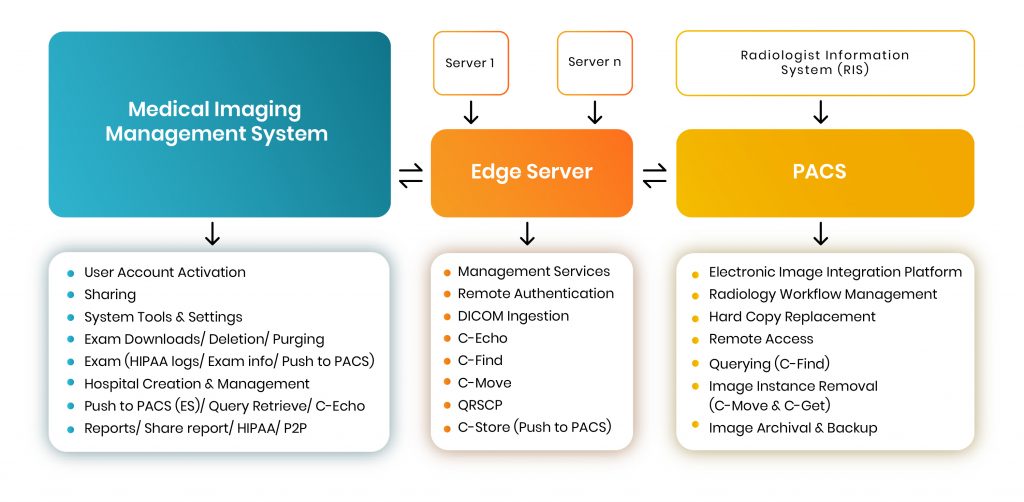
A Typical HIPAA-compliant Medical Imaging Management System places a request (for a specific file) to ‘PACS’ via an intermediary system known as ‘Edge Server’. The sole purpose of the Edge Server is to function as a request-node so that other hospitals or physicians can contact the particular radiologist (who possesses the images stored in PACS) and place a request to access a copy of the file in question.
[Related: Modern Medical Enterprises Absolutely Need Test Automation. Here’s Why.]
Medical image sharing use cases
Critical use cases arise for medical image sharing involving support for:
- Remote image viewing (out of network)
- Specialist consults
- Telehealth (examples such as teleburn, telestroke)
- Trauma transfers
- Ambulatory image review
Typically, PACS store digital medical images locally for retrieval. A PACS consists of four major components:
- The imaging modalities such as X-ray plain film (PF), CT and MRI
- a secure network for the transmission of patient information
- workstations for interpreting and reviewing images
- archives for the storage and retrieval of images and reports.
To communicate with the PACS server we use DICOM messages that are similar to DICOM image ‘headers”, but with different attributes. The Edge Server manages several functions that allow users to sort through hundreds of thousands of large-volume data and retrieve a specific file from a database either stored in ‘PACS’ or on the ‘MIMS’.
Each of the three highlighted sections (see diagram) can perform various functions, while communication is defined through specific rules and standards that are legally enforced and universally followed.
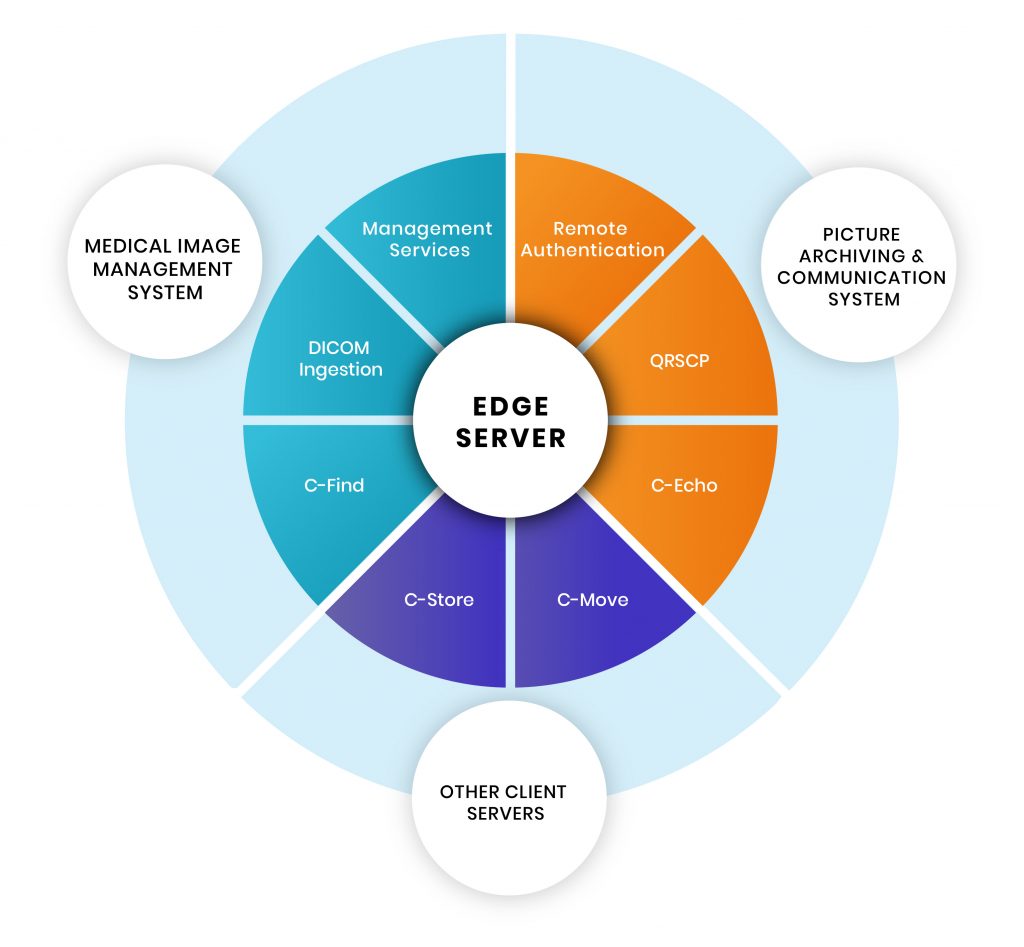
Through the ‘Edge Server’, we can access images stored in PACS. The ‘Management Services’ operation is the first and foremost feature. It means that a user can control & maintain the complete functionality of the server through this. Using ‘Remote Authentication’, users can obtain centralized authorization and authentication to request files from PACS. Please note, Remote Authentication is a networking protocol operating by way of specific ports.
To verify basic DICOM connectivity to the server — i.e, to check if the server is live or not, a C-Echo message is sent to ping the server, after which it will wait for its response. Once identifying the server as live, a user can perform querying and retrieval-based operations. Next, the user can begin the process of requesting DICOM images from the Medical Image Management System — known as ‘Ingestion’. DICOM Ingestion involves pre-assigned IP and port addresses (default ports are 2104-2111).
Basic DICOM Operations
Client: First, it’s important to check the location of the specific image(s) on a particular server. For this, a query-based C-FIND operation sends a request to the server. The user establishes a network connection to the PACS server and prepares a C-FIND request message (which is a list of DICOM attributes). The user then fills in the C-FIND request message with ‘keys’ that match. (E.g. to query for a patient ID, the user fills the patient ID attribute with the patient’s ID.) Then, the C-FIND request message is sent to the server.
Server: The server reverts a list of C-FIND response messages. Each of these messages contain a list of DICOM attributes with values for each match. It then initiates C-MOVE request using the DICOM network protocol to retrieve images from the PACS server.
One can retrieve images at the Study, Series or Image (instance) level. The C-MOVE request specifies where the retrieved instances should be sent (using separate C-STORE messages). The C-STORE operation, also known as DICOM Push simply pushes (sends) the images to the PACS server (or P2P — Push to PACS).
C-STORE message implements the DICOM storage service. The SCU sends a C-STORE-RQ (request) message to the server, which includes the actual dataset to transfer. The server answers by returning a C-STORE-RSP (response) message to the user, communicating success or failure of the storage request.
DICOM Images Benefits
Using DICOM images, health management professionals, physicians, and radiologists can utilize secure protocols in handling confidential medical image data. It extends the ability to view such images discreetly and instantly; avoiding duplication costs; and reducing unnecessary radiation exposure to patients.
Medical Image Sharing furthers the “Health 2.0” initiative by being able to instantly and electronically exchange medical information between physicians, as well as with patients — improving communication within the industry.
[Related: How AI is innovating healthcare sector?]
About the author: Rijin Raj is a Senior Software Engineer-QA at Mantra Labs, Bangalore. He is a seasoned tester and backbone of the organization with non-compromising attention to details.
Related:
- Test Automation Services
- Regression Testing in Agile: A Complete Guide for Enterprises
- Modern Medical Enterprises Absolutely Need Test Automation. Here’s Why.
- Basics of load testing in Enterprise Applications using J-Meter
- [Part 1] Web Application Security Testing: Top 10 Risks & Solutions
- [Part 2] Web Application Security Testing: Top 10 Risks & Solutions
DICOM FAQs
DICOM stands for — Digital Imaging and Communication. It is a medical standard for sharing a patient’s MRI, X-ray, and other image files over the internet.
Unlike regular images (png, jpg, etc.) DICOM is a secure format for storing confidential medical images. Usually, PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) and MIMS (Medical Image Management System) are used to store DICOM Images.
DICOM is used for securely storing and retrieving confidential images in distributed networks (internet).
Using DICOM images, health management professionals, physicians, and radiologists can securely handle confidential medical image data.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




